Why Is Night Sleep Important? A Deep Dive Into Sleep, Hormones, and Health
Sleep is more than just rest—it’s essential for memory, hormone production, muscle repair, and overall mental and physical health. Every night, while we sleep, our body works hard to restore and recharge itself.
Let’s explore why night sleep matters so much, what happens to your body when you skip it, and how you can improve your sleep naturally.
What Makes Night Sleep So Crucial?
Throughout the day, our brain processes countless pieces of information. But it’s during the night—while we sleep—that these memories get stored in the long-term memory bank. Similarly, muscle and protein synthesis also occur while we sleep.
For men, testosterone—a key hormone for energy, muscle strength, and sexual function—is released only after 3 continuous hours of sleep.
That’s why night sleep isn’t optional—it’s a core part of being healthy.
Are You Getting Poor Sleep?
Many people stay up late due to work, stress, or sleep issues. Ask yourself:
-
Do you struggle to wake up in the morning?
-
Feel tired or irritable during the day?
-
Lose focus easily?
-
Feel excessively hungry or snacky?
-
Lack motivation or energy?
If you said “yes” to even half of these, you may already be facing the short-term effects of poor sleep—commonly called insomnia.
What Regulates Our Sleep?
Two key processes control your sleep:
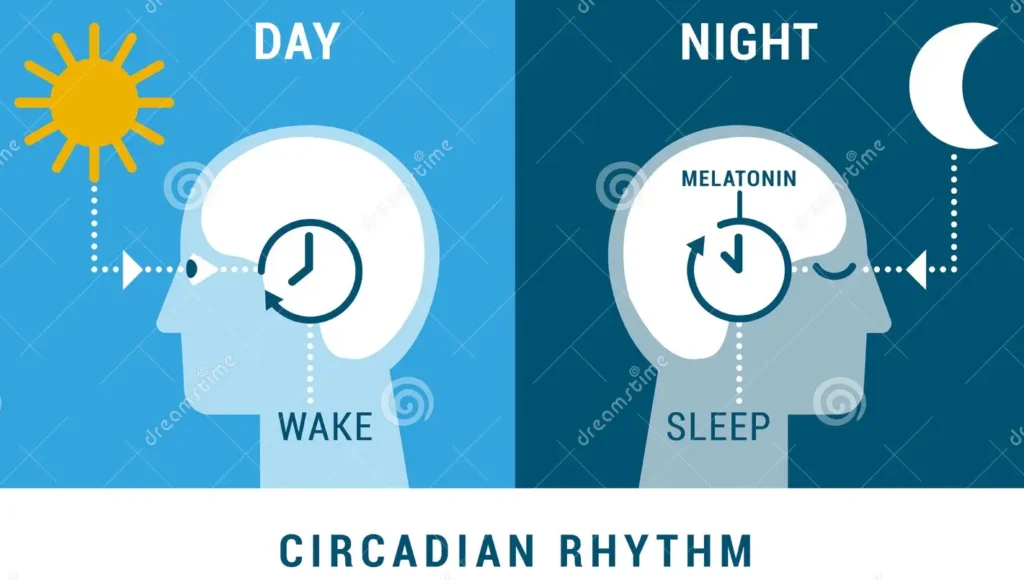
-
Circadian Rhythm (Body Clock):
Your natural day-night cycle, regulated by sunlight. -
Sleep Drive:
Just like hunger builds up if you haven’t eaten, the urge to sleep builds the longer you stay awake.
Understanding the Circadian Rhythm
Your circadian rhythm follows the sun. When it’s light out, your brain gets the signal to stay awake. As darkness falls, melatonin (a sleep hormone) is released, making you sleepy.
If you were to remove all artificial light from your environment, your body would naturally sync with the rising and setting sun.
We are biologically wired to sleep at night—not during the day.
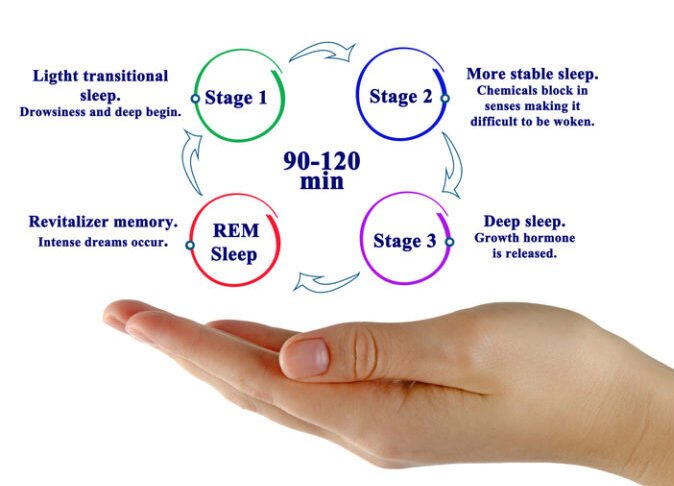
What Happens When You Sleep?

When you sleep at night, your body does amazing things:
-
Brain Repair: Your brain filters out unnecessary information and converts useful memories to long-term storage.
-
Stress Reset: Stress hormones reduce significantly, helping you feel calmer the next day.
-
Muscle & Tissue Recovery: Protein synthesis and cell repair happen, especially during deep sleep.
-
Immunity Boost: Your immune system strengthens.
-
Hormone Production: Testosterone and other crucial hormones are released.
-
Dream Phase (REM): Your muscles temporarily become paralyzed to prevent physical injury during dreams.
-
Kidney Function Adjusts: Urine production slows, helping you sleep through the night.
Have you noticed how you don’t feel the urge to urinate during the night? That’s your body prioritizing rest and preventing disturbances.
What Happens When You Don’t Sleep?
Skipping night sleep reverses all these benefits:
-
High Stress: Cortisol (stress hormone) levels rise.
-
Increased BP & Heart Risk: Blood pressure stays elevated, increasing the risk of heart disease.
-
Hunger Hormones Disrupted: Ghrelin and leptin go off balance, increasing appetite and cravings.
-
Weakened Immunity: You get sick more often.
-
Weight Gain: Fatigue lowers physical activity, metabolism slows, and food intake often increases.
-
Poor Focus & Memory: Brain fog, lack of clarity, and reduced productivity set in.
-
Low Testosterone & Libido: For men, lack of proper sleep impacts testosterone, affecting drive and performance.
-
Premature Aging & Risk of Chronic Disease: Poor sleep over time contributes to diabetes, depression, heart conditions, and early death.
How to Improve Night Sleep Naturally

To improve sleep, we must manage both circadian rhythm and sleep drive.
1. Align Your Body Clock (Circadian Rhythm)
Avoid artificial light before bed. Here’s how:
-
Turn off bright lights 1–2 hours before sleep.
-
Dim your bedroom lights in the evening.
-
Avoid screens (phones, laptops, TV) before bed.
-
Let natural sunlight wake you in the morning.
This keeps your internal clock in sync with nature, which is essential for quality rest and better health.
2. Build Your Sleep Drive

You’ll sleep better when your body wants to sleep. To build that drive:
-
Avoid afternoon naps.
-
Stay physically active during the day.
-
Stick to a routine: Sleep and wake up at the same time every day.
-
Avoid mentally stimulating activities before bed—like watching intense shows, scrolling social media, or working.
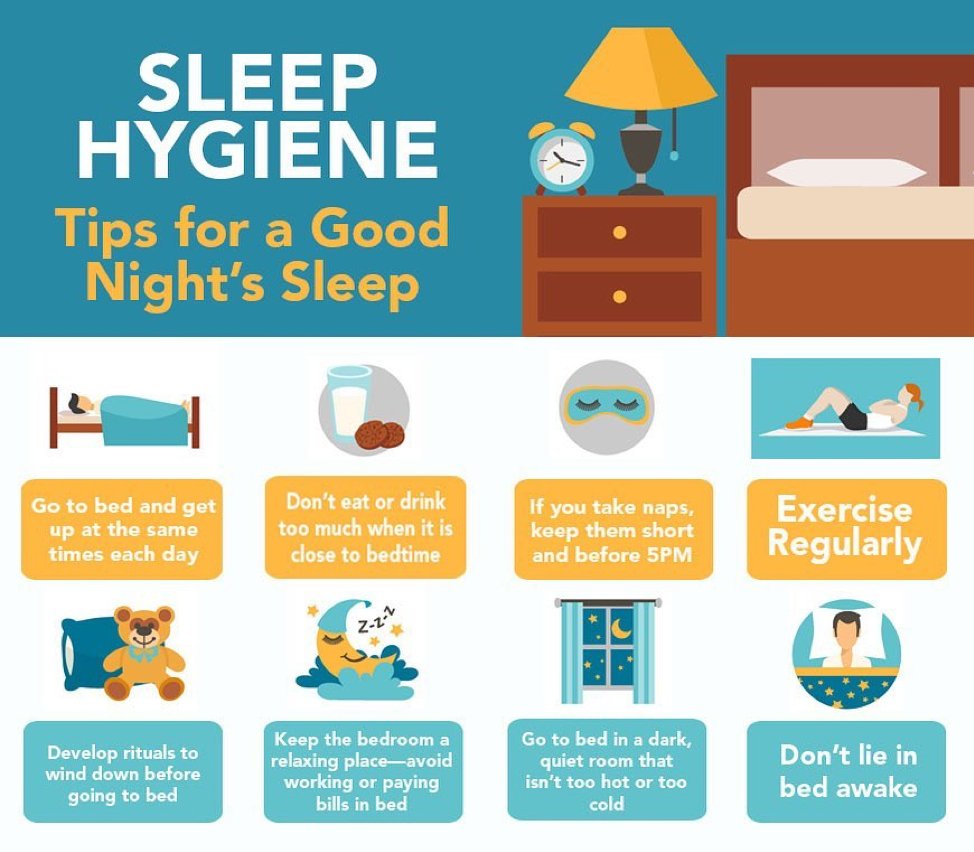
Optimizing Your Sleep Environment (Sleep Hygiene)

Your surroundings play a big role in sleep quality. Make your bedroom:
-
Dark: Use blackout curtains or eye masks.
-
Quiet: Use earplugs or white noise if needed.
-
Cool & Comfortable: Keep the room temperature pleasant.
-
Clean: Fresh bed linens and a tidy room help relax the mind.
Avoid:
-
Caffeine and chocolate in the evening—they stimulate the brain.
-
Heavy workouts just before bed—they raise adrenaline levels.
-
Stressful thoughts or content—try reading or listening to soothing music instead.
Optional: Take a warm shower before bed—it helps activate the body’s relaxing system and preps you for a deep, restful sleep.
Final Thoughts
Night sleep is the foundation of your physical health, mental clarity, hormonal balance, and emotional well-being. It’s not just about how many hours you sleep—but when and how.
By aligning with your natural rhythms, managing light exposure, and improving your bedtime habits, you can reclaim deep, restorative sleep and enjoy better health every day.